问题由来
来新公司也大半年了,发现之前的工程实现的非常不合理,维护成本极高,内部吐槽严重,BUG 叠 BUG,修老 BUG 引入的新 BUG 层出不穷,质量堪忧。
Pros & Cons
拿到代码后简单的看了一下:
- 使用
MVC模式,并且由于各种原因,说白了就是写的挫。将MCV(Model-View-Controller)写成了MVC(Massive View Controller) View Controller写的极为笨重,几乎流程都写在几个比较大的View Controller中。牵一发而动全身,能不出错么。- 目前的时机比较不错,新项目要开始了,及得想办法复用之前的逻辑,又得写的没什么问题。
- 很久不写这种流程了,还是需要仔细的回归练习一下,而且还能练练 swift,何乐而不为呢
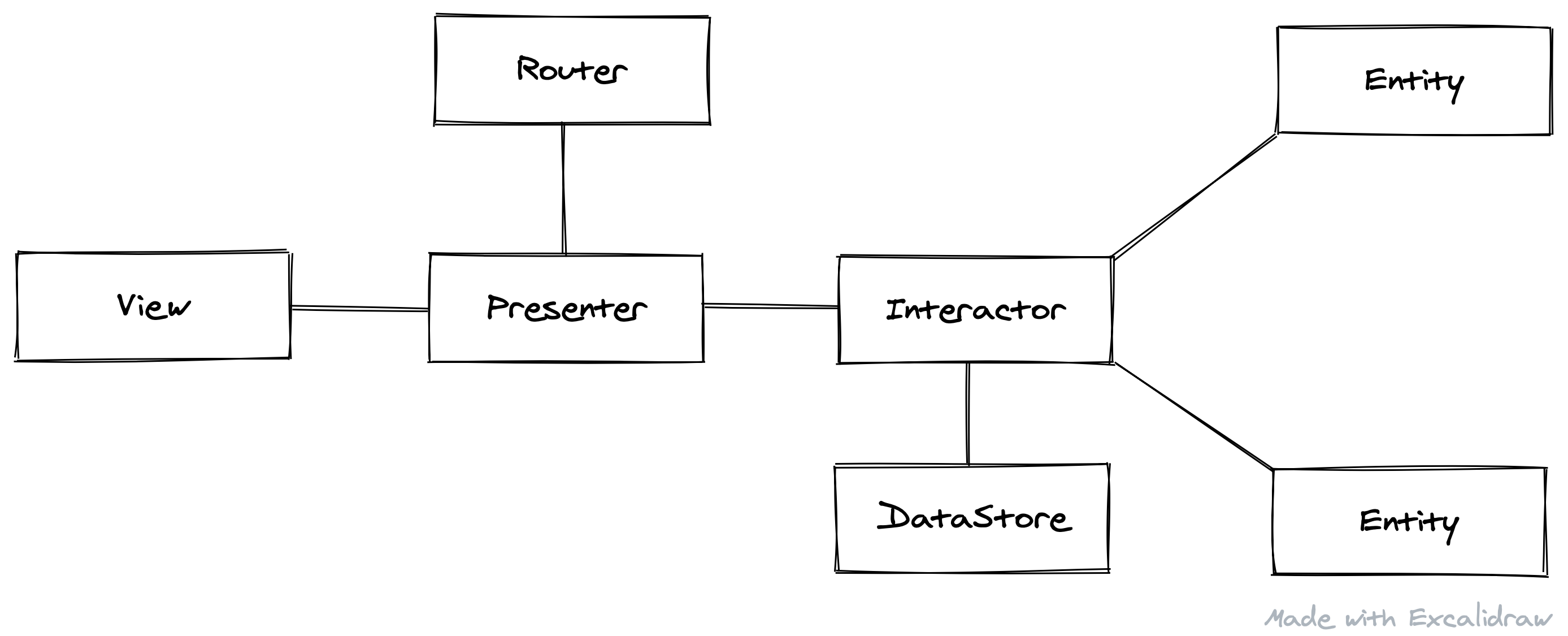
VIPER 结构简介
VIPER 是视图 (View),交互器 (Interactor),展示器 (Presenter),实体 (Entity) 以及路由 (Routing) 的首字母缩写。这样根据逻辑结构的不同可以划分为不同的责任层。使得依赖更容易隔离,比如说数据库,也更容易单独测试,边界清晰。
他们的关系大概是这样的 如下图所示:
为什么要用 VIPER
互联网企业都要求快速迭代,要求周期短,质量高。如何快速的在满足需求的前提下下交付质量好的产品,是大家都想解决的问题。对于一个处于一线的程序员来讲,从根上推动整个流程的变化是不切实际的。比较稳妥且的办法是采用技术手段来提高自己的效率,降低出错的概率。
对于源源不断的需求,以及不断的需求变化。除了默默的问候这些 PM,不还是得一个字一个字的敲出来。做的不好,大家会怀疑你的能力。面子上挂不住。活那么多,身体抗不住,身为一个快乐的程序员,在减少秃头的情况下得想办法让自己轻松点嘛。
步入正题
- VIPER 的好处就是模块之前关系比较松散,模块划分清晰,几乎做到了彻底解耦。每个(VIPER)子模块都可以单独的测试,
- 避免掉了 MVC -> M(assive)VC 的情况,VC 里面几乎就是个接口调用,几乎就是完成业务流程的胶水代码,而且都是 Protocol 的接口,业务比较清晰。
- 数据模型的处理,单独的放到了 Interactor 内部,这一块对于其他模块几乎是透明。
- VC 彻底细化为View 和 Presenter,三者的交互可以参考 MVP 模式,不多说。
- Router 作为业务的入口和跳转的枢纽,将跳转逻辑也吃掉了。
- 最终 VIPER 化之后,代码量会变多、文件会变多,逻辑变得清晰可维护。
- 不同的 VIPER 模块 通信只有两个途径,一个是通过 ROUTER,另一个是通过 INTERACTOR
开始落地
设计图
VIPER 模板
每次手工新建五个文件着实比较蛋疼,那么使用 XCode 模板每次自动新建不是很爽。链接就是新建好的模板。方便省事,目前只有 Mac 版本,改吧改吧 iOS 版本也不是啥难事以聊天页为例 VIPER 落地
- 从图中可以看到该页面比较简单,聊天页面大概分两个部分,左边应该是 thread 列表,右边是 消息流。
- 窗体的样式几乎都是自定义的。
- 顶部存在多 TAB,方便切换不同的显示内容。
- 由于是 IM,那就存在登陆和非登陆,因此需要目前两个 VIPER 模块。
- 从设计来看,各种 UI 组件都需要自定义,因此需要提供一个 UI 基础组件库,给工程提供子弹。吃掉 UI 的内部细节。只要对外提供行为即可。
登陆 VIPER 结构
登陆需要简单的输入用户名和密码,然后呢对于登陆成功的状况,会有账户维护和消息同步。
设计有要求在登录页内部玩各种花活。因此目前沟通后,登录页划分为登陆输入页,和登陆行为页,两个页面的逻辑和流程不大一样。
登陆输入页的协议定义如下
1 | |
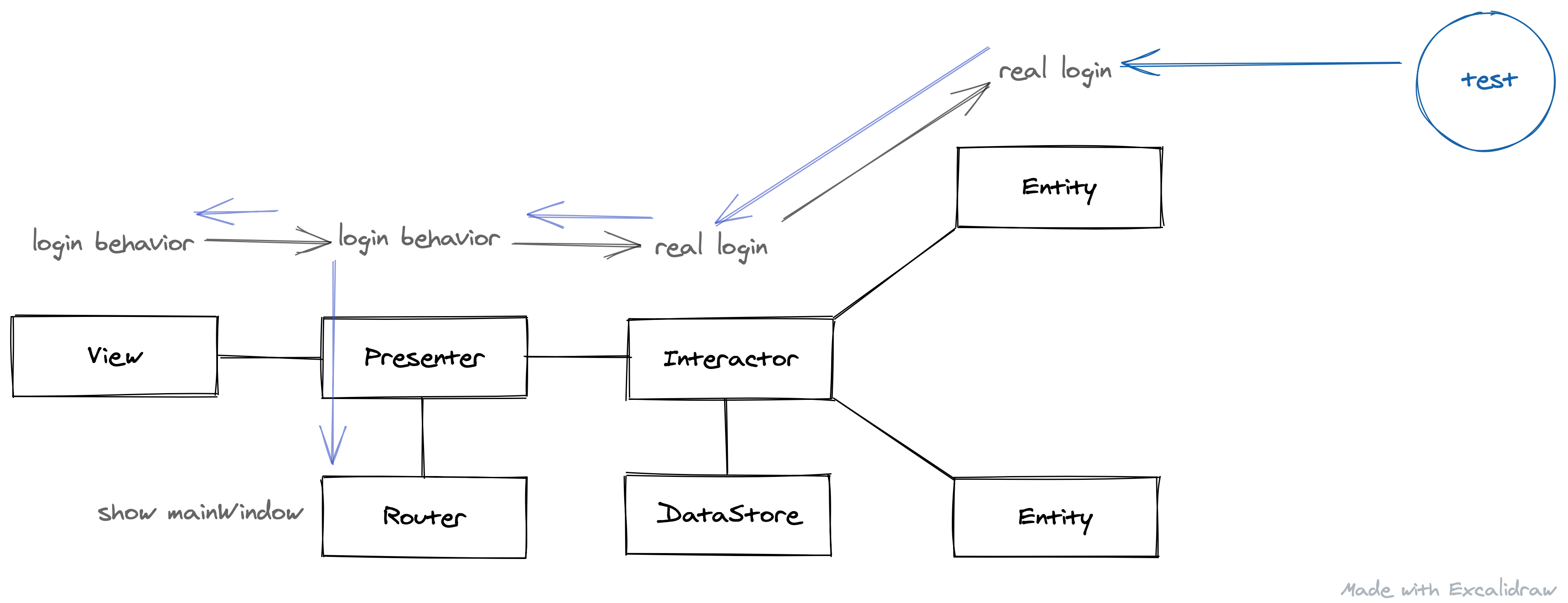
- 登陆行为页
1 | |
一个简单的功能,写了这么多是不是很蛋疼,明明只需要一个 VC 就可以搞定的事情,非得这么麻烦么?
其实在真正实现之后,发现除了文件多点以为,登陆的逻辑和流程非常清晰,真正地做到了代码自解释,不同结构之间通过接口来实现交互。将与其他模块无关的功能对外隐藏,而且真正的收益是在整个工程的逻辑和功能变得越来越复杂之后才体现出来。
聊天 VIPER
登陆成功后,界面会由登陆 VIPER 模块路由到主界面 VIPER,如下图,那么界面就可以正常的切换过来了
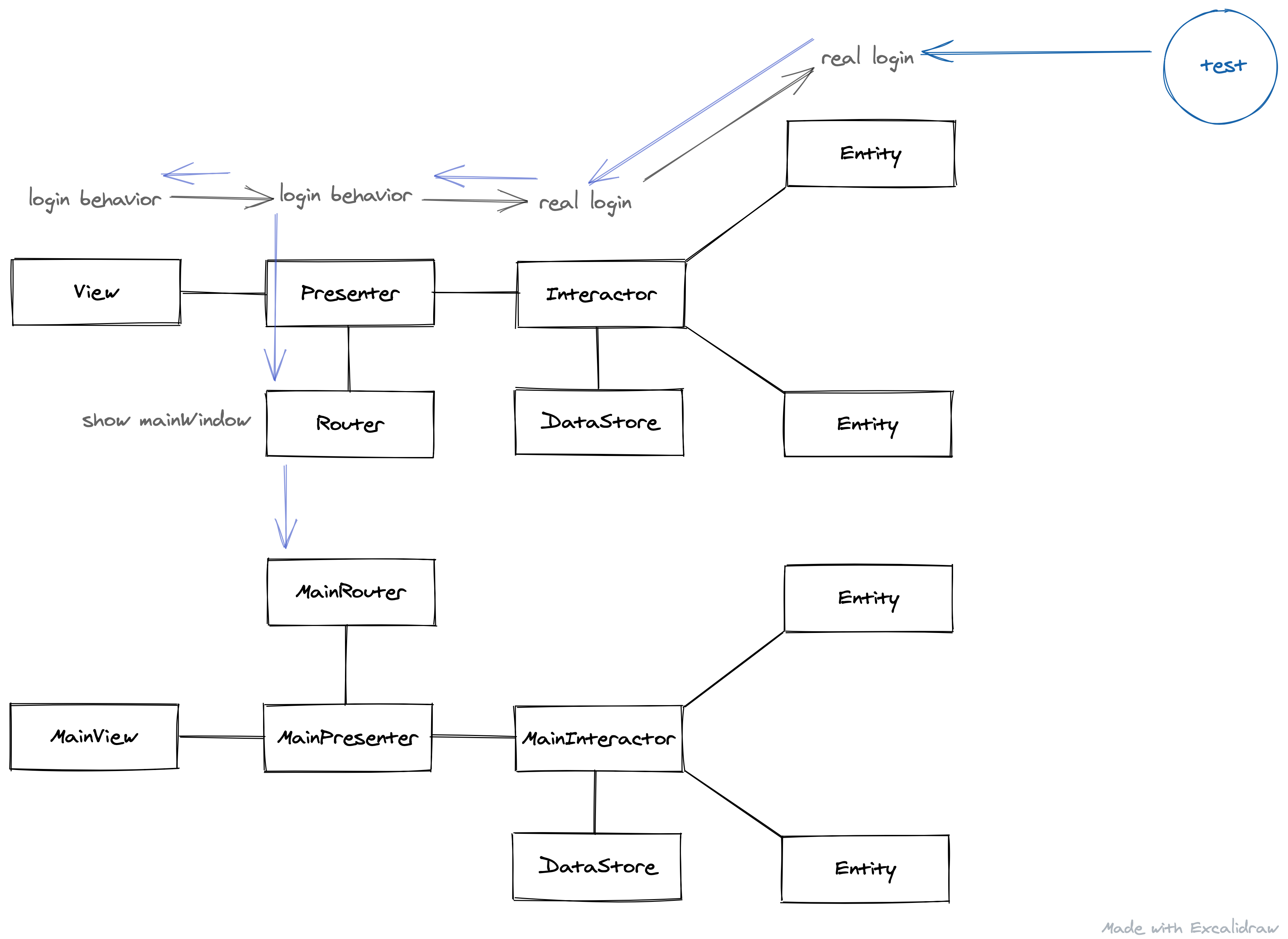
- 搭建几个重要 VIPER 子结构
通过分析具体的业务流程和要完成的功能 不断地补充接口,篇幅问题,省略掉大部分细节,以切换 tab 为例。
1 | |
随着功能的逐渐叠加,VIPER 中不同的子结构的代码增加都很平稳,不会出现某一个模块代码量指数级的增加。
从前任写完的第一个版本的 bug 叠 bug,到这个版本的内部备受好评,其实基础功能都一致,只不过是界面看上去有着巨大的差别。但是从结果来看维护成本和收益都很不错,但实际上改变的是整个项目的基础结构,开发流程,并且带动了大家往着更合理的方向前进 。
从这个过程中,内部总结出了,代码规范,提交规范,开发规范,这么看来,每个人都应该有着不少的收获.
